|
|
Electron transport chain
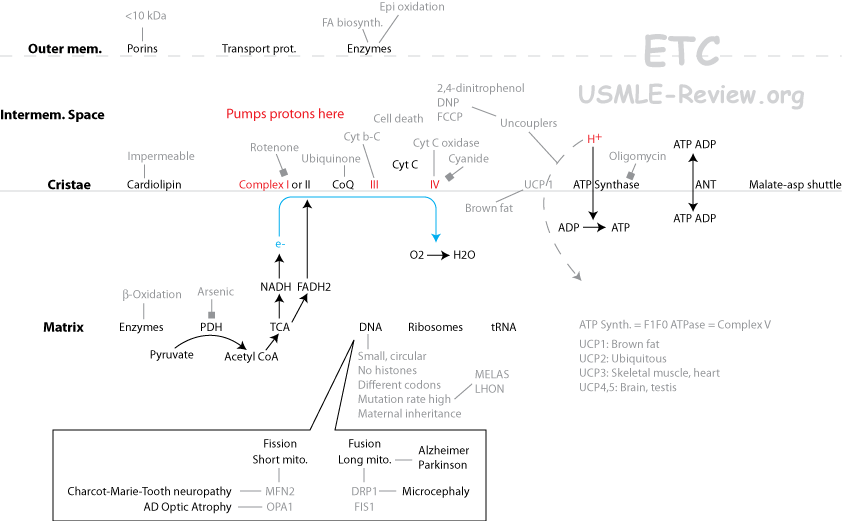
Electron transport: pumps protons into intermembrane space
- Complex I
- Receives electrons from NADH.
- Transfers electrons to CoQ.
- Inhibited by rotenone, amytal.
- Complex II
- Receives electrons from FADH2.
- Transfers electrons to CoQ
- Coenzyme Q
- Also called ubiquinone, or CoQ.
- Transfers electrons to complex III.
- Complex III
- Transfers electrons to cytochrome c.
- Inhibited by antimycin A.
- Cytochrome c
- Transfers electrons to complex IV.
- Complex IV
- transfers its electrons to oxygen, forms water.
- Inhibited by CN-
Oxidative phosphorylation: uses proton gradient to make ATP
- Complex V, also called ATP Synthase.
- Oxidative phosphorylation occurs here, turning ADP to ATP.
- Uses the proton gradient generated by electron transport.
- Inhibited by oligomycin.
- 2,4-DNP, aspirin, thermogenin increases membrane permeability. Causes proton gradient to leak through membrane rather than fuel ATP synthase.
Aerobic Cellular Respiraction: Glucose + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
- Glycolysis: Glucose → 2 Pyruvate (2ATP, 2NADH)
- Krebs Cycle: 2 Pyruvate → 6 CO2 (8NADH, 2FADH2, 2GTP)
- 3 CO2 per pyruvate.
- 4 NADH per pyruvate.
- 1 FADH2 per pyruvate.
- 1 GTP per pyruvate.
- At the end of the Krebs cycle, the C6 glucose has been fully oxidized to 6 molecules of CO2.
- Electron transport chain: 6O2 → 6H2O (28ATP)
- 3 ATP per NADH.
- 2 ATP per FADH2.
- Summary: 36 ATP + 2 GTP per glucose.
- Glycolysis: 2 ATP.
- Krebs Cycle: 2 GTP.
- ETC: 34 ATP.
- 2 NADH from glycolysis: 2 x 3 = 6 ATP.
- 8 NADH from Krebs cycle: 8 x 3 = 24 ATP.
- 2 FADH2 from Krebs cycle: 2 x 2 = 4 ATP.
Mitochondrial transport
- Glycerol phosphate shuttle: NADH → mitochondria: 2ATP/NADH, found in most cells with mitochondria, regenerates cytosolic NAD+
- Malate-aspartate shuttle: NADH → mitochondria: 3ATP/NADH, found in heart, regenerates cytosolic NAD+
- Oxaloacetate out of mitochondria by conversion to either malate (malate DH) or aspartate (aspartate aminotransferase).
- Tricarboxylate transport system: Acetyl CoA out of mitochondria. Mechanism: transport citrate (made from acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate) into the cytosol, where it's broken back down to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate.
- ATP-ADP translocator: ATP out of mitochondria, ADP into mitochondria, driven by membrane potential.
- Atractyloside and Carboxyatractyloside inhibit translocator on the external surface.
- Bongkrekic acid inhibits translocator on the internal surface.
- Phosphate carrier: returns inorganic phosphate back into the mitochondria.
|
|
