|
|
Normal processes
- embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
- organ structure and function
- hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary gland
- thyroid gland
- parathyroid glands
- adrenal cortex, adrenal medulla
- pancreatic islets
- ovary and testis
- adipose tissue
- cell/tissue structure and function, including hormone synthesis, secretion, action, and metabolism
- peptide hormones
- steroid hormones, including vitamin D
- thyroid hormones
- catecholamine hormones
- renin-angiotensin system
- repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal processes
- infectious, inflammatory, and immunologic disorders (eg, subacute thyroiditis, Graves disease,
sarcoidosis)
- traumatic and mechanical disorders
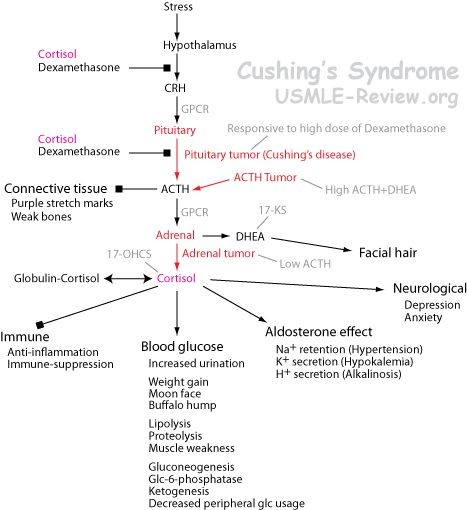
- neoplastic disorders (eg, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal cortex, pancreatic islets, neural crest,
pheochromocytoma)
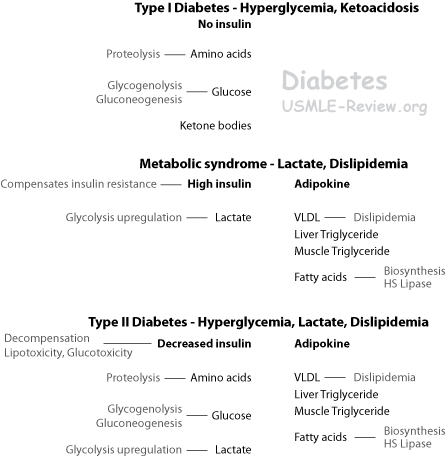
- metabolic and regulatory processes (eg, diabetes mellitus, pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid,
parathyroid, pancreatic islet disorders, adrenal disorders)
- vascular disorders (eg, pituitary apoplexy)
- systemic disorders affecting the endocrine system
- idiopathic disorders (eg, hirsutism)
Principles of therapeutics
- mechanisms of action, use, and adverse effects of drugs for treatment of disorders of the endocrine
system
- hormones and hormone analogs
- stimulators of hormone production (eg, sulfonylureas)
- inhibitors of hormone production (eg, thiouracils)
- hormone antagonists
- potentiators of hormone action (eg, thiazolidinediones)
- antiobesity agents
- other therapeutic modalities (eg, surgery, radiation)
Gender, ethnic, and behavioral considerations affecting disease treatment and prevention, including psychosocial,
cultural, occupational, and environmental
- emotional and behavioral factors (eg, compliance in diabetes mellitus, factitious use of insulin, psychogenic
polydipsia)
- influence on person, family, and society
- occupational and other environmental risk factors (eg, radiation exposure, iodine deficiency)
- gender and ethnic factors
|
|