|
|
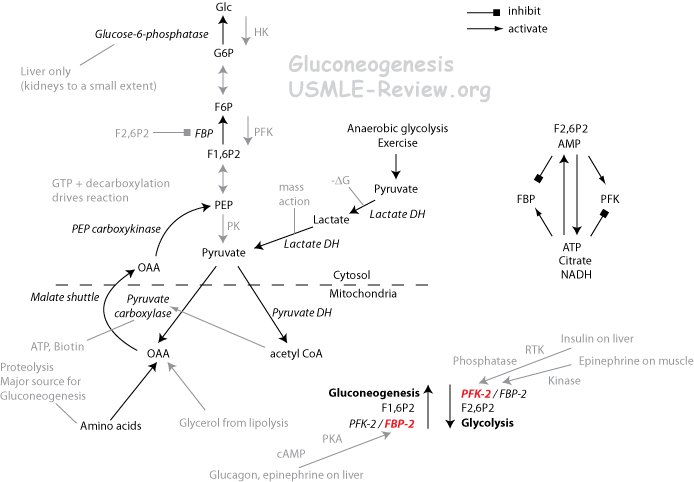
- Pyruvate carboxylase: Pyruvate → Oxaloacetate
- Biotin as prosthetic group for the carboxyl group transfer.
- Avidin, found in raw egg whites, binds biotin and inhibit its intestinal absorption.
- Activated by acetyl-CoA.
- ATP hydrolysis.
- Oxaloacetate transported out of mitochondria as aspartate by shuttle.
- PEP Carboxykinase: Oxaloacetate → PEP
- GTP hydrolysis and decarboxylation drives reaction.
- Fructose bisphosphatase: F1,6BP → F6P
- Inhibited by F2,6P (which stimulates glycolysis).
- Activated by ATP, citrate
- High blood glucose: insulin released by pancreas, dephosphorylates PFK-2/FBP-2 to make PFK-2 active, ↑ F2,6P, glycolysis occurs.
- Low blood glucose: glucagon released by pancreas, phosphorylates PFK-2/FBP-2 to make FBP-2 active, ↓ F2,6P, gluconeogenesis occurs. In muscles, epinephrine causes phosphorylation of PFK2/FBP2 causes PFK2 to be active, which makes F2,6BP and activates glycolysis.
- Main regulatory step.
- Glucose-6-phosphatase: G6P → Glucose
- Found only in liver, so gluconeogenesis in liver produces blood glucose.
- Deficiency of gluconeogenesis causes hypoglycemia.
- What feeds into gluconeogenesis: lactate (Cori cycle by lactate DH), amino acids (citric acid cycle), glycerol (fat).
- Occurs in the liver when blood sugar is low (fasting)
|
|
