|
|
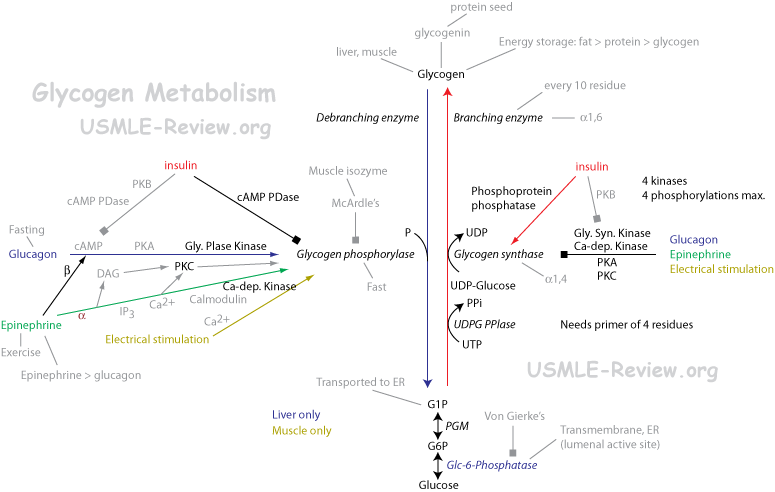
Glycogenolysis
- Glycogen phosphorylase
- Glycogenn → glycogenn-1 + G1P
- Cleaves 1-4 linkage.
- Can't touch residues near branch point.
- Deficient in McArdle's disease (type V glycogen storage disease) in skeletal muscles. Symptoms: muscle exertion lead to painful cramps and muscle damage.
- Glycogen debranching enzyme:
- Transfers 1-4 linkage from near branch point somewhere else.
- Cleaves 1-6 linkage for the last branch point residue to make glucose.
- Deficient in Cori's disease (type III glycogen storage disease). Symptoms: milder version of type I.
- Phosphoglucomutase:
- Glucose-6-phosphatase:
- Converts G6P → glucose.
- Deficient in Von Gierke's disease (glycogen storage disease type I). Symptoms: hepatomegaly, ↑ liver glycogen that can't be broken down to glucose → severe hypoglycemia and ↑ blood lactate.
- Lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase:
- Glycogen → glucose (in lysosome).
- Deficient in Pompe's disease (type II glycogen storage disease). Symptoms: cardiomegaly, systemic findings leading to early death.
Glycogenesis
- UDP-Glucose pyrophosphorylase: makes UDP-Glucose.
- UDPG Pyrophosphorylase: G1P + UTP → UDPG + PPi
- Pyrophosphatase: PPi → 2 Pi
- Nucleoside diphosphate kinase: UDP + ATP → UTP + ADP.
- Glycogen synthase: makes 1-4 glycogen linkage by adding UDP-Glucose.
- Glycogen branching enzyme: transfers a 1-4 to 1-6.
- Also called amylo-(1,4→1,6)-transglycosylase.
|
|
