|
|
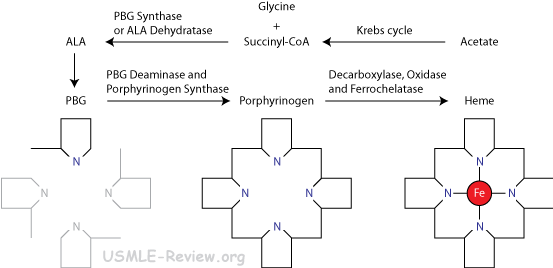
- Porphyrins are made entirely from Glycine and Succinyl-CoA (derived from acetate).
- ALA = δ-Aminolevulinic acid.
- PBG = Porphobilinogen.
- Occurs partly in the mitochondria and partly in the cytosol (PBG synthase, PBG deaminase, uroporphyrinogen III synthase, uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase)
- Porphyrias: accumulation of porphyrins due to defects in heme biosynthesis.
- Congenital erythropoietic porphyria: Uroporphyrinogen III synthase deficiency results in accumulation of uroporphyrinogen I and coproporhyrinogen I. Makes urine red, teeth red, skin photosensitive + ulcers, hair on faces and extremities.
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria: Ferrochelatase deficiency results in accumulation of protoporphyria, causing itching, pain, photosensitivity, nerve damage.
- Acute intermittent porphyria: PBG deaminase deficiency results in accumulation of PBG and ALA (excreted in urine), causes intermittent abdominal pain, neurological dysfunction, causes red urine, photosensitivity.
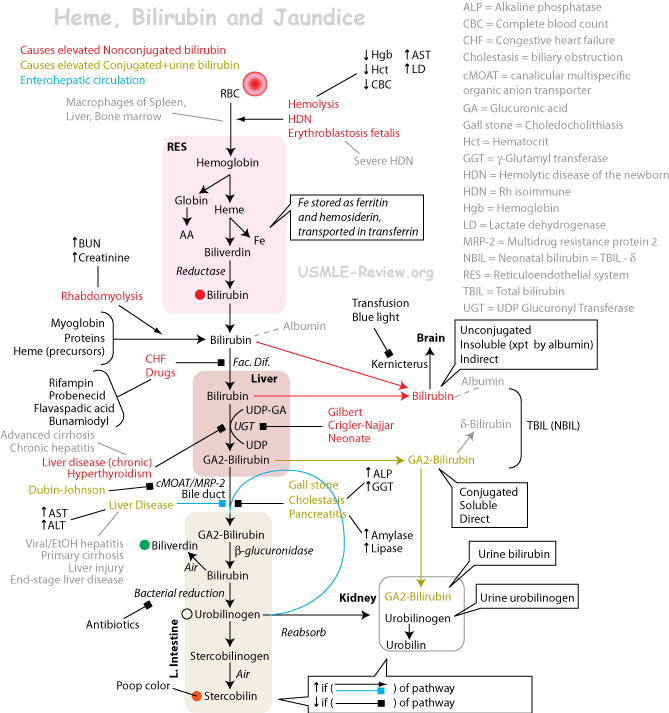
- Aged, damaged RBCs are destroyed in Liver, Spleen and Bone marrow.
- Hemoglobin → Heme + Globin (this protein is then degraded to amino acids).
- Heme → Biliverdin → Bilirubin → Urobilinogen → Stercobilin → excreted in feces.
- Bilirubin travels in blood complexed with albumin.
- Too much bilirubin in blood causes jaundice. Caused by increased RBC destruction, liver dysfunction, or bile duct obstruction.
- Liver esterifies bilirubin to bilirubin diglucuronide to make it more soluble, and secretes it in bile. If bile duct obstructs, then bilirubin accumulates.
- Some urobilinogen is reabsorbed, transported to kidney, where it's converted to urobilin, which gives urine its yellow color.
- Stercobilin gives feces their brown color.
|
|
