|
|
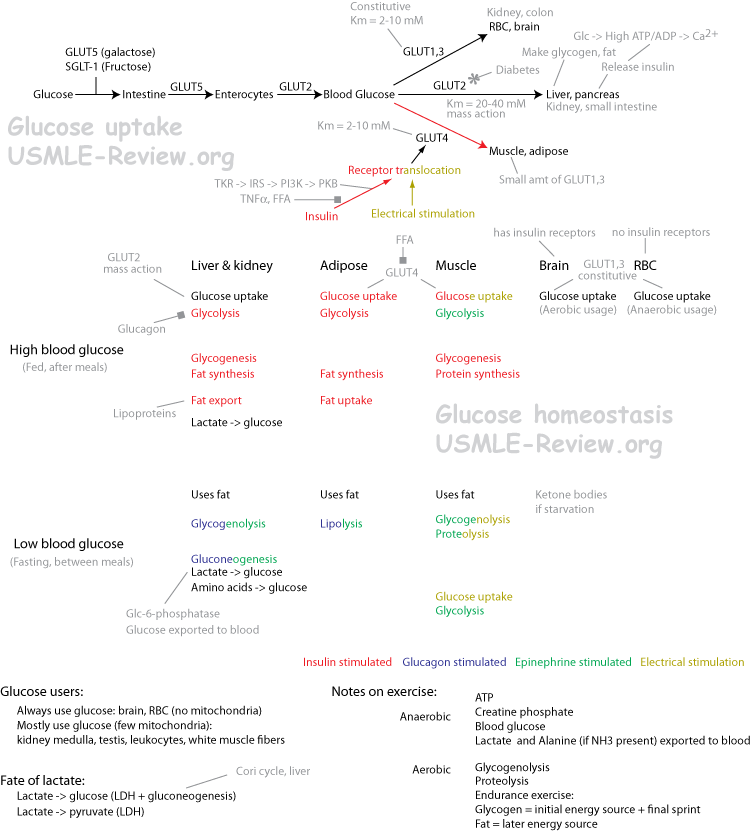
nutrition
- generation, expenditure, and storage of energy at the whole-body level
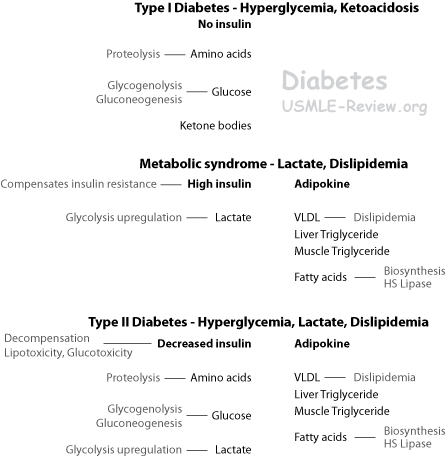
Diabetes
- assessment of nutritional status across the life span, including calories, protein, essential
nutrients, hypoalimentation
- functions of nutrients, including essential, trans-fatty acids, cholesterol
- protein-calorie malnutrition
- vitamin deficiencies and/or toxicities
- mineral deficiencies and toxicities
- eating disorders (eg, obesity, anorexia, bulimia, alternative diets and nutritional supplements, treatment)
temperature regulation
adaptation to environmental extremes, including occupational exposures
- physical and associated disorders (eg, temperature, radiation, burns, decreased atmospheric pressure,
high-altitude sickness, increased water pressure)
- chemical (eg, gases, vapors, smoke inhalation, agricultural hazards, volatile organic solvents,
heavy metals, principles of poisoning and therapy)
fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance and disorders (eg, dehydration, acidosis, alkalosis)
|
|