|
|
Normal processes
- embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
- organ structure and function
- female structure, including breast
- female function (eg, menstrual cycle, puberty, menopause)
- male structure
- male function (eg, spermatogenesis, puberty)
- intercourse, orgasm
- pregnancy, including ovulation, fertilization, implantation, labor and delivery, the puerperium,
lactation, gestational uterus, placenta
- cell/tissue structure and function, including hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, sex steroids, and
gestational hormones
- reproductive system defense mechanisms and normal flora
Abnormal processes
- infectious, inflammatory, and immunologic disorders (eg, toxic shock syndrome, breast abscess,
orchitis, sexually transmitted diseases, autoimmune hypogonadism, cystic mastitis)
- traumatic and mechanical disorders (eg, female incontinence, prolapse, cystocele, torsion of testis, varicocele,
circumcision, phimosis)
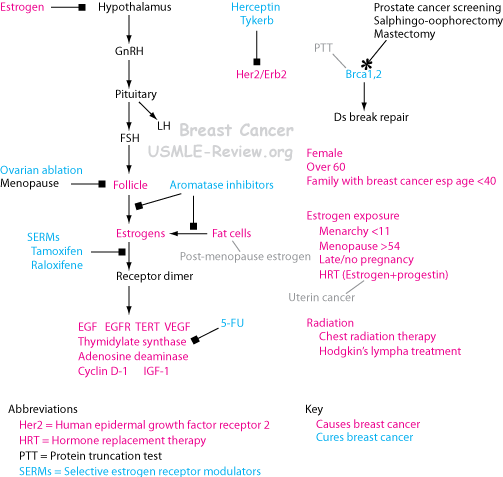
- neoplastic disorders (eg, female reproductive, male reproductive, breast [including fibrocystic
changes], trophoblastic disease)
- metabolic and regulatory processes
- female (eg, anovulation, infertility, polycystic ovaries, endometriosis, orgasmic dysfunction,
delayed and premature puberty, menopausal syndrome)
- male (eg, infertility, impotence, gynecomastia, delayed and premature puberty, benign prostatic
hyperplasia)
- systemic disorders affecting reproductive function (eg, obesity, myotonic dystrophy, cirrhosis, renal
failure)
- disorders relating to pregnancy, the puerperium, and the postpartum period
- obstetric problems (eg, ectopic pregnancy, third-trimester bleeding)
- complications affecting other organ systems (eg, eclampsia, gestational diabetes, thyroid
disorders)
- disorders associated with the puerperium (eg, postpartum hemorrhage, sepsis, depression)
- antepartum, intrapartum, postpartum disorders of the fetus (eg, prematurity, postmaturity, cord
compression, macrosomia)
Principles of therapeutics
- mechanisms of action, use, and adverse effects of drugs for treatment of disorders of the
reproductive system and management of normal reproductive function
- female reproductive tract
- fertility drugs
- oral contraception, other methods of contraception (eg, condoms)
- estrogen, progestogen replacement, treatment of menopause
- stimulants and inhibitors of labor
- estrogen and progesterone antagonists
- stimulators and inhibitors of lactation
- male reproductive tract
- fertility drugs
- androgen replacement and antagonists
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin replacement
- abortifacients
- antimicrobials
- antineoplastics
- restoration of potency
- other therapeutic modalities affecting the reproductive system (eg, tampons)
Gender, ethnic, and behavioral considerations affecting disease treatment and prevention, including psychosocial,
cultural, occupational, and environmental
- emotional and behavioral factors (eg, sexually transmitted diseases)
- influence on person, family, and society (eg, infertility)
- occupational and other environmental risk factors (eg, radiation)
- family planning and pregnancy (eg, unwanted)
- gender identity, sexual orientation, sexuality, libido
- effects of traumatic stress syndrome, violence, rape, child abuse
|
|