|
|
Fructose, Galactose and Mannose Metabolism
- Fructose intolerance:
- Aldolase B deficiency causes accumulation of F1P
- Depletes liver phosphates, no phosphate no glycogenolysis
- ATP drops so no gluconeogenesis. Activates glycolysis, causes lactic acidosis.
- Hypoglycemia because of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis inhibition.
- Jaundice, cirrhosis, vomiting.
- Develops distaste for sweet stuff.
- Essential fructosuria:
- Fructokinase defect causes fructose to appear in urine.
- Benign because fructose doesn't enter cells.
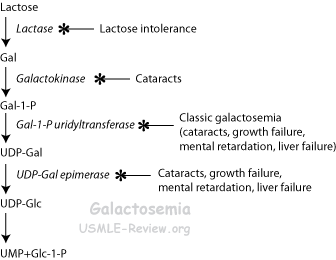
- Classical Galactosemia:
- Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase defect causes accumulation galactose (appears in blood, urine, reduced to galactitol in lens).
- Galactose enters eye, aldose reductase changes it to galactitol (can't leave).
- Galactitol accumulates in lens and causes cataracts (Diabetics have glucose → sorbitol which causes cataracts).
- Failure to thrive, jaundice, hepatomegaly, infantile cataracts, mental retardation.
- Treatment: no galactose or lactose (glucose and galactose).
- Enzymes involved in galactose → glucose:
- Galactokinase: Gal → Gal-1-P. Deficiency causes ↑ galactose (cataracts).
- Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase: Gal-1-P → UDP-Gal. Deficiency (classic galactosemia) causes ↑ galactose (cataracts) + Gal-1-P (growth failure, mental retardation, liver damage).
- UDP-Gal epimerase: UDP-Gal → UDP-Glc. Deficiency of which causes ↑ galactose (cataracts) + Gal-1-P (growth failure, mental retardation, liver damage) + UDP-Gal.
- Lactose intolerance: lactase deficiency (blacks, asians lose brush-border enzyme). Lactose = Gal-Glc, dietary source of galactose.
|
|
