|
|
Tissue types
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscle
- Nerve
Epithelial

- Simple squamous: for diffusion, filtration.
- Simple cuboidal and columnar: for absorption and secretion.
- Stratified squamous: for protection against abrasion.
Gland epithelia
- Endocrine: ductless, hormones.
- Exocrine: all other nonhormone glands, like sweat, mucus, digestive enzymes.
- Structure of exocrine glands
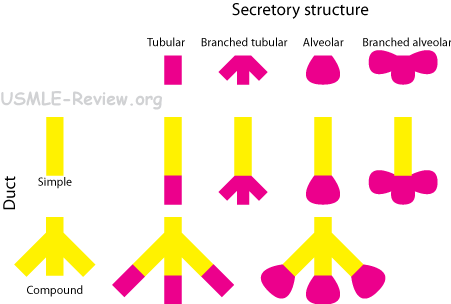
- Merocrine: secrete by exocytosis. Eg, pancreas, saliva.
- Holocrine: secrete by rupture. Eg, oil glands.
Connective
- Connective tissue = cell + a lot of extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Cell = -blast + -cyte
- -blast if immature, actively secreting matrix
- -cyte if mature, less active in secretion
- ECM = ground substance + fibers
- ground substance: interstitial fluid, adhesion molecules, proteoglycans
- fiber: collagen (strong, tendens, ligaments), elastic (skin, lungs, blood vessels), reticular (net-like, basement membrane).
- All connective tissue are derived from mesenchyme of embryo.
Connective tissue types
- Connective tissue proper (fibroblasts)
- Loose (areolar, adipose, reticular)
- Areolar: connective tissue underneath epithelia
- Adipose: fat tissue
- Reticular: lymphoid tissues: lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen
- Dense (regular, irregular, elastic)
- Regular: tendens, ligaments
- Irregular: dermis of skin, submucosa of digestive tract, covering of organs and joints.
- Elastic: elastic ligaments connecting adjacent vertebrae.
- Cartilage (chondroblasts)
- Hyaline cartilage: embryonic skeleton, ends of long bones, costal cartilages, nose, trachea, larynx
- Elastic cartilage: ear, epiglottis
- Fibrocartilage: inverterbral discs, pubic symphysis, knee
- Bone (osteoblasts)
- Blood (hematopoietic stem cells)
Muscle
| Skeletal | Cardiac | Smooth |
| Voluntary, striated, multinucleated | Involuntary, striated, branched, uni-binucleated | Involuntary, smooth, uni-nucleated |
| Endomysium (cell), perimysium (fascicle), epimysium (organ) | Endomysium | Endomysium |
| Sliding filaments organized in sarcomeres | Sarcomeres | Sliding filaments forms spiral net on sacolemma. Actin (predominant over myosin) network attached to the dense bodies on sarcolemma |
| Troponin on actin | Troponin on actin | No troponin, actin always ready. Calmodulin makes myosin head bind to actin in the presence of calcium. |
| Attach to bones via tendons | | Attach to tissues via dense bodies on sarcolemma |
| Contraction causes shortening of tissue | Squeezing | Longitudinal layer: dilates, shortens tissue. Circular layer: constricts, elongates tissue. Alternate of the two leads to peristalsis. |
| T-tubules propagate action potential deep into cell, stimulate SR to release calcium | Same as skeletal muscle, but also takes in extracellular calcium | Caveolae takes in extracellular calcium (SR contributes some to calcium release also) |
| No gap junctions | Gap junctions, synchronize contraction | Gap junctions, synchronize contraction |
| Aerobic (red), Mix (pink), Anaerobic (white) | Aerobic | Aerobic |
Nervous tissue
- Nervous tissue = neuroglia + neurons
- Neuroglia (gial cells):
- CNS:
- Atrocytes: spans neurons and capillaries, makes exchanges.
- Microglia: macrophage.
- Ependymal cells: line central cavities of brain and spinal cord. Cilia circulates CSF.
- Oligodendrocytes: myelin sheaths.
- PNS:
- Satellite cells: surround neuron cell bodies.
- Schwann cells: myelin sheaths, neurilemma.
- Neurons
- Cell body (perikaryon, soma): no centrioles, well developed RER (nissl bodies) and Golgi.
- Dendrites: receiving end, graded potentials.
- Axon: transmitting end, action potentials, axolemma.
- Axon terminals: secretory region, neurotransmitters.
Neuron types
- Multipolar: many dendrites, one axon. Most abundant, major neuron in CNS, mostly interneurons and motor neurons.
- Bipolar: one dendrite, one axon. Rare, found in sensory nerves of nose, eye, ear.
- Unipolar: one axon. Found mainly in PNS, afferent sensory nerves.
|
|
