|
|
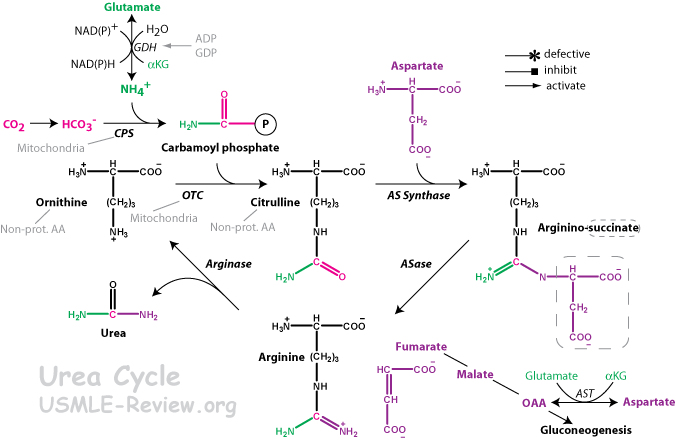
Enzymes
- AT = Aminotransferase = transaminase
- GDH = Glutamate dehydrogenase
- CPS = Carbamoyl phosphate synthase
- OTC = Ornithine transcarbamoylase
- AS Synthase = Argininosuccinate synthase
- ASase = Arginosuccinase
- PC = Pyruvate carboxylase = enzyme in glucogenesis.
- Fumarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate uses enzymes in krebs cycle.
Deamination of N-terminal Amine
- Aminotransferase
- Takes N-terminal amine of amino acid and places it on αKG to make glutamate. Aka. Transamination.
- Requires PLP (pyridoxal-5-phosphate), which is derived from pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
- Glucose-alanine cycle
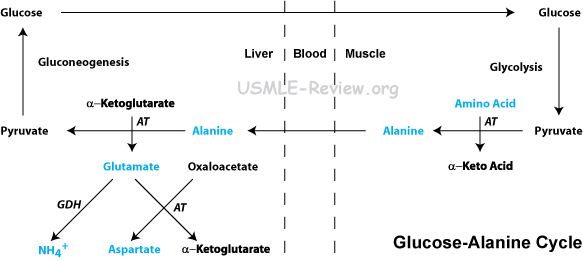
- Amino acids in muscle passes amino group to alanine, which travels to liver and passes the amino group on to glutamate.
- Glutamate dehydrogenase
- Accepts either NAD+ or NADP+.
- Activated by NAD+, ADP, Leucine.
- Inhibited by NADH, GTP.
- Amino acid oxidase
- Amino acid → NH4+ + α-keto acid (uses FAD and H2O)
- Some amino acids are deaminated non-oxidatively (something other than α-keto acid results)
Urea Cycle
- What goes in: NH4+ + HCO3- + Aspartate
- What comes out: Urea + Fumarate
- Urea gets one amino group from NH4+, the other form aspartate, and the carbon atom from HCO3-. Fumarate is derived from the carbon skeleton of aspartate.
- 3 ATP hydrolyzed: CPS converts 2ATP → 2ADP. AS Synthase converts ATP → AMP.
|
|
